Understanding Negative Synergy: The Hidden Pitfalls of Mergers and Acquisitions
7 Tips for Managing Negative Synergy in an M&A Process
Navigating a business liquidity event can be a complex process regardless of the size or nature of your business. In this article, Capstone Partners’ Transaction Advisory Services Team shares steps you can take to position your business for success and outlines seven recommendations to identify and mitigate common causes of negative synergy.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are often pursued for the potential positive synergies they can bring, such as increased market share, enhanced operational efficiencies, and expanded product portfolios. However, the darker side of these transactions, characterized by negative synergy, frequently gets overlooked.
Negative synergy—collectively dis-synergies—can erode value, disrupt operations, and lead to significant financial losses. Understanding and anticipating these pitfalls is crucial for any successful M&A strategy.
While few companies are willing to publicize negative synergies, a study by consulting firm AON revealed a concerning trend in employee engagement following company acquisitions. Among the acquiring companies, the percentage of actively disengaged employees increased from 13% to 18%, while actively engaged employees decreased from 10% to 7%, according to the 2013 report.¹ These negative shifts are even more pronounced in the acquired businesses, where actively disengaged employees rose from 13% to 21%, and actively engaged employees plummeted from 10% to 5%. This stark decline in engagement is likely to lead to decreased productivity, lost profits, and an exodus of employees, highlighting significant challenges in maintaining employee morale and organizational stability post-acquisition.
Common Types of Negative Synergy in M&A
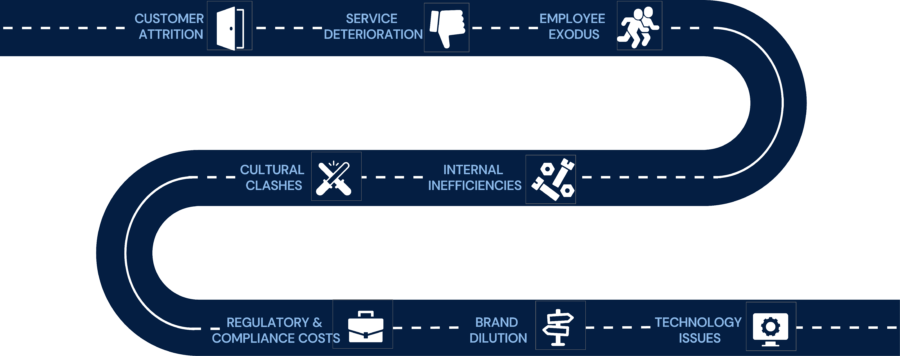
Customer Attrition
When two companies merge, especially large ones, existing customers might feel uncomfortable with the increased concentration of their business with a single vendor. This can lead to a loss of shared accounts as customers seek alternatives to avoid dependency on one supplier. For example, a merger might cause customers to fear reduced negotiation power or decreased service quality, prompting them to switch to competitors.
Service and Fulfillment Deterioration
Post-merger integration challenges can result in disruptions to customer service and order fulfillment. Inconsistent service levels and delayed deliveries can erode customer trust and loyalty, leading to lost sales. The complexity of merging different systems and processes often exacerbates these issues, causing operational inefficiencies.
Employee Exodus
M&A activities can create uncertainty and anxiety among employees, leading to higher turnover rates. When key personnel leave, they might take crucial client relationships with them, jeopardizing key accounts. This can be particularly damaging in industries where personal relationships and trust are integral to business success, such as consulting or investment banking.
Internal Inefficiencies
Integrating IT (information technology), finance, and HR (human resources) systems from different companies can be complex and costly. Redundant systems and conflicting processes can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and a slower decision-making process. For instance, incompatible IT infrastructures may require expensive overhauls or result in ongoing operational disruptions.
Cultural Clashes
Differences in corporate culture between merging entities can lead to conflict and reduced productivity. If employees from each company have vastly different working styles or values, it can result in reduced collaboration and efficiency. The clash between Amazon’s (Nasdaq: AMZN) efficiency-driven culture and Whole Foods’ customer-focused values post-acquisition is a notable example of this issue.²
Regulatory and Compliance Costs
Mergers can also bring about increased regulatory scrutiny and compliance costs, especially in highly regulated industries. This can lead to delays and additional expenses that were not initially anticipated. Regulatory hurdles and prolonged investigations can significantly impact the timeline and success of the integration process, not to mention the associated legal costs.
Regulators challenged at least $361 billion of global transactions announced in 2022 and 2023, according to a study conducted by Bain & Company.³ The collective value of those that closed that required a remedy to address regulators’ concerns was $255 billion. The total regulatory compliance costs were not explicitly stated but it is reasonable to expect a deduction in value for each individual transaction challenged because of both direct expenses like legal fees and indirect impacts from delays in integration and overall business disruption.
Brand Dilution
Combining two companies with strong, distinct brands can lead to confusion among customers and weaken brand loyalty. If not managed carefully, the brand equity of one or both companies can suffer, leading to a loss of customer trust and market position. For example, merging companies may struggle to maintain consistent branding and messaging, which can alienate existing customers and hinder the acquisition of new ones.
Technological Integration Issues
Merging companies with different technological infrastructures can face significant challenges in integrating their IT systems. These issues can lead to data migration problems, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and disruptions in day-to-day operations. The cost and complexity of aligning technological platforms can also drain resources and divert attention from core business activities.
7 Recommendations for Managing Negative Synergy
1. Do Your Homework
Thorough due diligence should include an assessment of potential dis- synergies. This involves evaluating the compatibility of corporate cultures, systems, and customer bases. Identifying potential areas of conflict and challenges early on can help in developing strategies to mitigate these risks. For example, understanding cultural differences can inform the development of integration plans that address these issues proactively.
2. Make Realistic Projections
Financial models should incorporate conservative estimates for cost savings and revenue enhancements, taking into account potential disruptions and inefficiencies during the integration process. By setting realistic expectations, companies can avoid overestimating the benefits of the merger and better prepare for any unforeseen challenges. This includes accounting for potential customer attrition and increased operational costs due to integration efforts.
3. Keep the Core Team
Develop and implement strategies to retain key employees, such as offering retention bonuses or clear career progression paths, to minimize the loss of talent and associated customer accounts. Retention plans should be communicated clearly and early in the process to alleviate employee concerns and prevent turnover. Additionally, fostering a sense of inclusion and participation among employees from both companies can help in building a cohesive post-merger culture.
4. Communicate
Proactively communicate with customers about the merger, highlighting the benefits and addressing any concerns they may have. Maintaining open lines of communication and providing reassurances can help retain customer loyalty. For instance, companies can reach out to key customers individually to discuss how the merger will benefit them and address any specific concerns they may have. Transparency in communication can also help in managing customer expectations and reducing uncertainty.
5. Invest Time in Integration Planning
Create detailed integration plans that outline the steps for combining systems and processes. This should include timelines, responsible parties, and milestones to ensure a smooth transition. Effective integration planning involves setting clear objectives, identifying potential risks, and developing contingency plans to address any issues that may arise. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the integration plan can help in addressing challenges promptly and keeping the integration on track.
6. Monitor and Adjust
Continuously monitor the integration process post-merger and be prepared to make adjustments as necessary. Regular progress reviews can help identify issues early and allow for timely interventions. Companies should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the success of the integration and measure the impact of negative synergies. By staying agile and responsive, companies can mitigate the impact of dis-synergies and ensure a successful integration.
7. Understand and Mitigate Regulatory Risks
Mergers often attract regulatory scrutiny, which can lead to delays and additional costs. To mitigate these risks, companies should:
- Proactively engage with regulatory bodies early in the M&A process to understand potential concerns and requirements. This can help in addressing issues before they escalate and in building a cooperative relationship with regulators.
- Conduct regulatory impact assessments to understand the regulatory implications of the merger. This includes analyzing antitrust issues, compliance with industry-specific regulations, and potential impacts on market competition.
- Develop compliance strategies to address regulatory requirements and ensure compliance. This can involve setting up dedicated compliance teams, implementing robust monitoring systems, and seeking legal counsel to navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
- Maintain transparent communication with all stakeholders, including regulators, investors, and Clear and honest communication can help in managing expectations and reducing uncertainty, which is crucial in maintaining trust and minimizing regulatory risks.
Conclusion
Factoring in negative synergy is crucial for the success of any M&A deal. By acknowledging and planning for potential pitfalls, companies can better navigate the complexities of integration and maximize the chances of achieving the desired outcomes. Incorporating these considerations into the deal model, alongside the more commonly highlighted positive synergies, provides a more realistic and balanced view of the transaction’s potential impact.
Anticipating and addressing negative synergies requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. By conducting thorough due diligence, setting realistic expectations, implementing effective retention and communication strategies, and continuously monitoring the integration process, companies can mitigate the impact of negative synergies and ensure a successful merger or acquisition. Understanding and mitigating regulatory risks also plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth transition and compliance with legal requirements.
Understanding and planning for negative synergies is not just about avoiding potential pitfalls; it is about maximizing the value of the deal and ensuring the long- term success of the combined entity. By taking a holistic view of the integration process and considering both positive and negative synergies, companies can create a solid foundation for growth and profitability in the post-merger environment.
The most successful M&A processes start with a comprehensive plan that identifies your transaction goals and creates an actionable road map to help your organization prepare for, execute, and integrate your deal strategy. Capstone’s Financial Advisory Services professionals have decades experience assisting clients through buy- and sell-side processes, as well working with them during the operational period to optimize profitability and efficiency. For more information on how Capstone’s Financial Advisory Services team can help preserve and accelerate your company’s value, please contact us.
Endnotes
-
AON, “Managing Employee Engagement During Times of Change,” https://www.aon.com/attachments/human-capital- consulting/2013_Managing_Engagement_During_Times_of_Change_White_Paper.pdf, accessed July 25, 2024.
-
Harvard Business School, “Amazon Whole Foods: When Cultures Collide,” https://hbswk.hbs.edu/item/amazon-vs- whole-foods-when-cultures-collide, accessed July 18, 2024.
-
Bain & Company M&A Report, “Regulation and M&A: How Scrutiny Raises the Bar for Acquirers,” January 30, 2024, https://www.bain.com/insights/regulation-m-and-a-report-2024/, accessed July 18, 2024.
Insights for Middle Market Leaders
Receive email updates with our proprietary data, reports, and insights as they’re published for the industries that matter to you most.